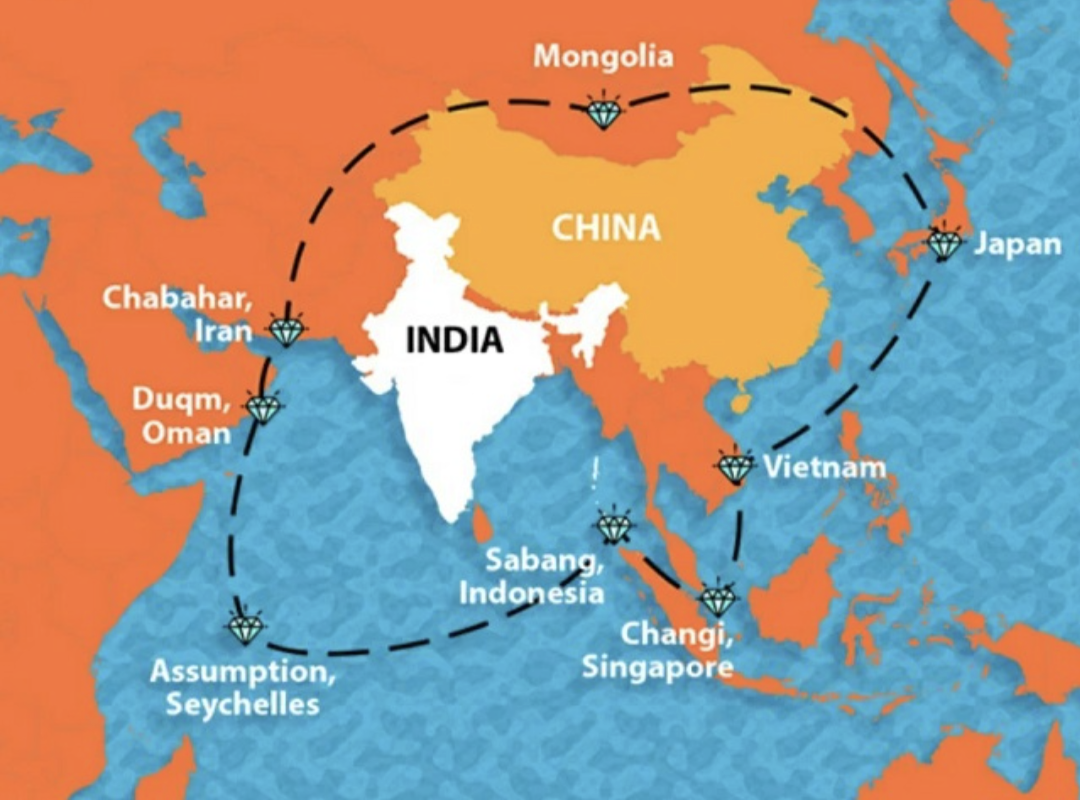
After realising China’s intentions of encircling India, India has began working on the Necklace of Diamonds, instead of being a mute spectator and watching China seize strategically located ports from the sidelines. India has started to fortify its presence in the Indian Ocean Region and has strengthened its security ties with the region’s countries. India believes it is the ‘net security provider’ in the region and any infiltration around the area will sabotage the Indian security.
To counter an aggressive China, India first made its presence at the Strait of Malacca, an important chokepoint in the region. India ramped up its presence in Singapore by signing the India-Singapore Bilateral Agreement, to secure the Changi naval base. India is also making strategic alliances with countries like Mongolia and Japan, which also have border disputes with China. India seeks to garland China, through its strategically located bases:
- Changi Naval Base, Singapore: In 2018, Prime Minister Modi signed an agreement with Singapore. The agreement has provided direct access to this base to the Indian Navy. While sailing through the South China Sea, the Indian Navy can refuel and rearm its ship through this base.
- Sabang Port, Indonesia: In 2018, India got the military access to Sabang Port which is located right at the entrance of Malacca Strait. This strait is one of the world's famous choke point. A large chunk of trade and crude oil passes on to China through this region.
- Duqm Port, Oman: Another feather was added to the cap when India got access to the Duqm Port in Oman. The Duqm Port is located on the south-eastern seaboard of Oman. The port facilitates India’s crude imports from the Persian Gulf. In addition to this, Indian facility is located right between the two important Chinese pearls-- Djibouti in Africa and Gwadar in Pakistan.
- Assumption Island, Seychelles: In 2015, India and Seychelles agreed upon the development of the naval base in this region. This gives military access to India. This base is of strategic importance to India as China desperately wants to increase its presence in Africa through the maritime routes.
- Chabahar Port, Iran: In 2016, Prime Minister Narendra Modi signed an agreement with Iran in 2016 to develop the Chabahar Port. The port provides access to Afghanistan and an important trade route to Central Asia.
##India’s Strategic Cooperation##
India is also developing new naval bases, developing the old bases and is developing its relations with other countries to garland China.
- Mongolia: Both the countries have agreed to cooperate to develop an air corridor, with the help of a credit line extended by India. To boost the bilateral relations, Prime Minister Modi was the first Indian Prime Minister to visit the country.
- Japan: The two countries have declared to build the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor. Also, the countries have flourishing bilateral relations and the two are also members of the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, a grouping aimed at countering China’s aggression in the Indo-Pacific.
- Vietnam: India has had a strong relationship with Vietnam, a country which was the recipient of India’s indigenously built Brahmos missile and 4 patrol boats.
- Central Asia: Prime Minister Modi visited all the 5 countries of Central Asia in one go and becomes the first Indian Prime Minister to do this. Within 4 years, trade with Central Asian countries has doubled after his visit.
India has maintained strong relationships with all the countries in China’s periphery, and with some of China’s rivals as well. This will give strategic access to India and the pattern can be seen as the necklace of diamonds garlanding China in a counter encirclement.